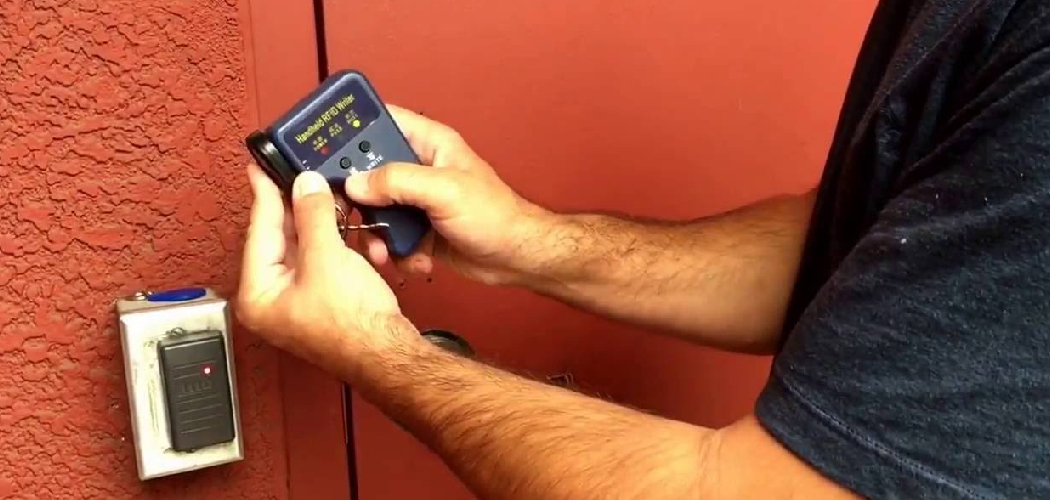
Key cards have become essential to modern security systems, often used for secure access in hotels, offices, and residential complexes. With varying types like RFID and magnetic stripe cards, each offers distinct advantages and application preferences.

However, the process of key card duplication is fraught with legal considerations. It’s crucial to understand that duplicating a key card without proper authorization is illegal and can lead to significant legal repercussions.
This article, “how to duplicate a key card,” emphasizes the legal duplication methods when authorization is given, such as for personal use or within a workplace setting. This guide aims to elaborate on the procedural steps for duplicating a key card safely, discuss the nuances of different types, and provide crucial precautions to ensure complete legality and security throughout the duplication process.
Understanding Key Card Types
A. Magnetic Stripe Cards
How They Work: Magnetic stripe cards store data on a magnetic strip that is swiped through a card reader. The strip contains magnetically encoded data, which determines access permissions. These cards are typically used in older systems and are known for their simplicity and ease of duplication, as the data they contain can be easily erased or overwritten.

Where They Are Used: Magnetic stripe cards are commonly found in hotels, older office buildings, and gyms. Their straightforward functionality makes them suitable for environments where high security is not the primary concern, though their susceptibility to wear and duplication can be a drawback.
B. RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) Cards
How They Work: RFID key cards feature an embedded chip that transmits a radio signal to a compatible reader when brought into proximity. This technology supports contactless access, allowing for more secure interactions by using unique identifiers that are significantly harder to replicate than traditional magnetic stripes.
Common Uses: Due to their enhanced security features, RFID cards are increasingly adopted in modern office buildings, parking garages, and apartment complexes. Their contactless nature and difficulty in duplicating make them ideal for settings where safety and convenience are prioritized.
C. Smart Cards
Advanced Features: Smart cards incorporate both a chip and a magnetic stripe, offering sophisticated security with advanced encryption capabilities. These features make duplicating them more challenging, although they can be cloned with appropriate equipment.

Usage: Smart cards are prevalent in high-security environments, such as government buildings or financial institutions, where data protection is paramount.
Legal Considerations for Duplicating a Key Card
A. Check Permissions and Authorization
Ownership and Consent: Before attempting to duplicate a key card, it is crucial to seek permission from the property owner or system administrator. Unauthorized duplication can breach trust and lead to criminal charges, placing civic responsibility and compliance at the forefront of your actions.
Employee or Tenant Responsibilities: As an employee or tenant, it is imperative to thoroughly review your lease or work contract to ascertain whether duplicating a key card is permissible. Many companies or property managers impose strict regulations prohibiting unauthorized card duplication, underscoring the importance of understanding and adhering to these policies.

B. Legal Consequences of Unauthorized Duplication
Potential Criminal Charges: Engaging in the unauthorized duplication of a key card can result in severe legal repercussions, including fines, lawsuits, or jail time, contingent on applicable local laws. This underscores the critical nature of observing legal guidelines in all duplication efforts.
Data Protection and Privacy: Given that many key card systems are integrated with personal data or secure information, unauthorized duplication poses significant privacy risks and can lead to serious security breaches. Protecting this data legally is essential to upholding privacy standards and preventing escalating legal issues.
Tools Required for Key Card Duplication
A. Magnetic Stripe Card Reader/Writer
How it Works: A magnetic stripe card reader/writer is a device used to extract the data encoded on a card’s magnetic strip and duplicate this information onto a blank card. It captures the encoded data through a swiping or inserting mechanism, enabling the user to clone the information onto a new card.

Where to Get It: These devices can be sourced from online retailers or specialty electronics stores. When acquiring a magnetic stripe card reader/writer, it’s crucial to ensure that it’s for legal and authorized purposes, as unauthorized use is prohibited and illegal.
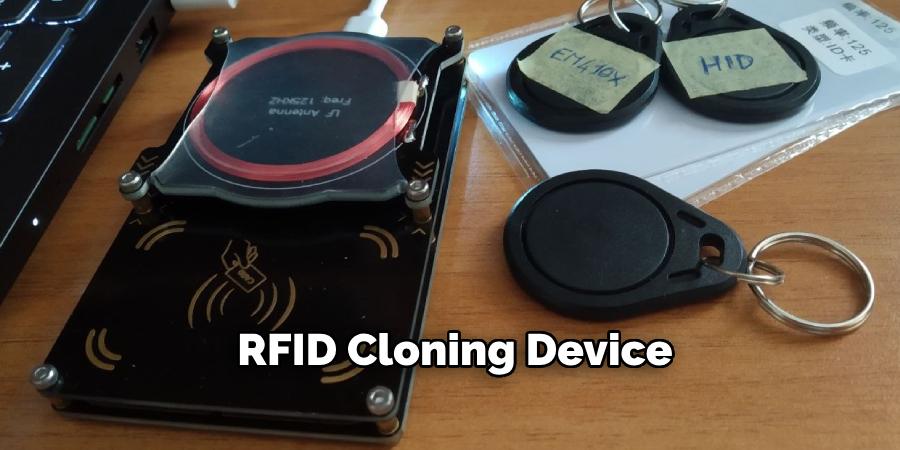
B. RFID Cloning Device
Purpose and Functionality: RFID cloning devices capture the unique identifier transmitted by an RFID key card. These devices read and store the data and can then duplicate it onto a blank RFID card or fob, facilitating replication.
Availability: These tools are typically more sophisticated and are used by professionals in the trade. They can legally be obtained from online marketplaces and specialty retailers, provided they are deployed with the proper authorization. Utilizing these tools without consent can result in legal issues due to their potential misuse.
C. Blank Key Cards
Required for Duplication: Blank magnetic stripe or RFID key cards are indispensable for duplicating data from an original card. They act as the recipient of the copied data. These blank cards are readily available from online platforms or security supply stores, ensuring users have the necessary materials for legally authorized duplication.
D. Smartphone Apps
RFID Duplication Apps: Some smartphone applications assert their capability to duplicate specific types of RFID cards. However, their efficacy may be inconsistent, contingent on the card type and phone model. Users must exercise caution regarding the legal and security implications, as unauthorized use might contravene legal standards.
How to Duplicate a Key Card: Duplicating a Magnetic Stripe Key Card
Step 1: Obtain the Right Equipment
Card Reader/Writer: To begin the duplication process, acquire a magnetic stripe reader/writer. You may choose to purchase or borrow one of these devices. To avoid any data mismatch, ensure it’s compatible with your specific card’s format. Research various models to confirm compatibility before making a purchase.
Blank Card: Next, secure a blank card that matches the type of card you wish to duplicate. This blank card should be of similar quality and format as the original to ensure the duplicated card functions properly once the data is transferred.
Step 2: Read the Original Card
Inserting the Original Card: With the reader/writer ready, swipe the original key card through the card reader. This action should capture the encoded data from the magnetic stripe and display it within the reader’s interface.
Save the Data: Ensure the data is stored securely by saving it to the device or transferring it to a secure digital location. It is crucial to handle this information with care to prevent unauthorized use or potential breaches of confidentiality.
Step 3: Write to a Blank Card
Insert the Blank Card: After securing the original data, proceed to insert the blank card into the writer. Utilize the saved information and initiate the writing process, embedding the original data onto the new card’s magnetic stripe.
Verify the Data Transfer: Once it is complete, immediately test the new card by swiping it through the reader/writer to confirm the data appears correctly. This verification step is essential to ensure the card works as intended, simulating the function of the original card.
Step 4: Test the Duplicated Card
Access Test: With the newly written card in hand, conduct an access test by using it in the lock or system it is intended for. Observe whether the card grants access and functions seamlessly, mirroring the performance of the original card.
Troubleshooting Issues: Should the card fail to function correctly, double-check the writing process and consider rewriting the data. Inspect the new card for compatibility issues, as some magnetic stripe cards integrate additional security measures that complicate easy duplication. Exploring alternative encoding methods or consulting with the device’s manual may also help resolve any issues. Ensuring that each step of the duplication and testing process is followed accurately can mitigate possible errors and guarantee the new card’s operational success.
How to Duplicate a Key Card: Step-by-Step Process
Step 1: Obtain an RFID Cloning Device
RFID Reader/Writer: Begin by purchasing or renting an RFID cloning device that aligns with the frequency of your key card, typically 125kHz or 13.56MHz. Ensuring that the device is compatible with your specific card type is crucial for the success of the duplication process.
Blank RFID Card or Fob: Additionally, procure a blank RFID card or fob that corresponds with the frequency and type of your original card. This blank card will serve as the new recipient for the copied data, making it essential to select a compatible option.
Step 2: Read the Original RFID Card
Scan the Original Card: Place the original RFID card on the reader, allowing the cloning device to capture its data. The device will scan and record the card’s unique identifier (UID) and any additional information.
Save the Information: Carefully store the captured data securely, protecting it against unauthorized access. Proper handling of this information will be indispensable during the subsequent writing stage.
Step 3: Write to a Blank RFID Card
Place the Blank RFID Card on the Writer: Position the blank RFID card or fob on the writer with the original card’s data securely saved. Initiate the data transfer process to embed the previously captured information onto the new card.
Confirm the Data Transfer: Upon completing the data transmission, verify that the UID and any other relevant data have been accurately copied. This confirmation step is essential to ensure the blank card functions identically to the original.
Step 4: Test the Duplicated RFID Card
Test for Proper Functionality: Utilize the duplicated RFID card at the intended access point to confirm its proper operation. Ensure it activates the system or unlocks the door seamlessly, mirroring the performance of the original card.
Troubleshooting RFID Duplication: Should the cloned card fail to function as expected, reassess the original card’s frequency and type to confirm compatibility. Be mindful that some systems might incorporate encryption measures, which may require additional tools or methods to bypass. In such cases, consulting the cloning device’s manual or seeking professional assistance may solve these challenges, ensuring successful duplication.
How to Protect Your Key Card from Being Duplicated
A. Use Encryption and Secure Systems
Advanced Encryption: Many modern key card systems incorporate encrypted data to thwart unauthorized duplication attempts. It’s vital to ensure that your key card system uses up-to-date encryption methods to safeguard sensitive information effectively. Regularly check for updates or upgrades to maintain the integrity and security of your system.
Choose Secure RFID Frequencies: Opt for higher-frequency RFID cards, such as 13.56MHz, which tend to offer more security compared to their lower-frequency counterparts. This upgrade can provide an additional layer of protection, so consider implementing it within your access control infrastructure if enhanced security is a priority.
B. Store Cards Safely
Protect from Scanners: Use an RFID-blocking wallet or sleeve to safeguard your key card from potential scans by unauthorized individuals. These protective accessories help prevent your card from being read or cloned without your consent, thus enhancing its security.
Limit Access: Avoid leaving your key card unattended and refrain from lending it to others. Unattended or loaned cards can be surreptitiously duplicated without your knowledge. Maintaining strict control over who has access to your card can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized duplication.
When to Call a Professional
A. High-Security Systems
Complex Encryption: When dealing with high-security systems that utilize complex encryption or other advanced security features, it may be necessary to call a professional to duplicate your key card. These systems often involve intricate coding that cannot be easily replicated without specialized knowledge.
Professional Locksmiths: Consider contacting licensed locksmiths or security experts who have the requisite tools and expertise to legally duplicate a key card. They are well-versed in handling more sophisticated systems and can ensure that the duplication process respects legal and technical constraints while maintaining the integrity of your security infrastructure.
B. Avoiding Damage to Systems
Preventing System Malfunctions: Improper duplication efforts can sometimes result in errors or damage to your access system, potentially compromising security and incurring costly repairs. In such instances, engaging a professional ensures that the duplication is performed meticulously and without harming the existing system. This precaution helps maintain the smooth operation and reliability of your security measures.

Conclusion
Successfully duplicating a key card involves a thorough understanding of the process, which includes using a magnetic stripe reader/writer or an RFID cloning device. Begin by ensuring compatibility between your cloning device and the key card’s frequency, followed by accurately copying the data onto a blank card or fob. It’s crucial to emphasize your legal responsibility throughout this process; you must have proper authorization before proceeding with any duplication, as unauthorized actions can result in serious legal consequences.
To maintain the security of your key card and prevent unauthorized cloning, consider investing in advanced security measures. Upgrading to encrypted systems and using RFID-blocking accessories can further protect your key card against potential breaches. By adhering to these guidelines and understanding how to duplicate a key card responsibly, you can ensure that your access control system remains secure and efficient.

